Shop for Plans
Shop for your own coverage
- Medical
- Dental
- Other Supplemental
-
(Cancer Treatment, Hospital Indemnity, and more)
Plans through your employer
- Learn about the medical, dental, pharmacy, behavioral, and voluntary benefits your employer may offer.
- Explore coverage through work
Learn
- How to Buy Health Insurance
- Types of Dental Insurance
- Open Enrollment vs. Special Enrollment
- See all topics
Living or working abroad?
- Shop for international insurance plans
Shop for Plans
Shop for Plans
Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Learn about standard breast cancer screenings, the stages and types of breast cancer, and how it's treated.
Breast Cancer Screening Tests
Breast cancer screenings are done regularly (often once a year, depending on your personal risk factors and health history). These are performed in order to detect breast cancer in people who don't have any signs or symptoms. Screenings are some of the best ways to detect breast cancer early.
Screening Mammogram
Clinical Breast Exam
Screening Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
If your provider notices something abnormal on your mammogram or during a breast exam, you may need to get more testing done.
Breast Imaging Techniques
Breast Biopsy
Types and Stages of Breast Cancer
Breast cancers are commonly divided into two categories: either non-invasive or invasive.
- The most common type of non-invasive breast cancer is called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). DCIS starts in the breast cells that line the milk ducts.
- The most common type of invasive breast cancer is invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC). This happens when cancer cells that start in the milk ducts change and spread into breast tissue outside of the duct and even beyond.
Typically, breast cancer is described with Roman numerals 0 through IV. A breast cancer stage tells you how much cancer is in your body. It can help your health team recommend the best treatment plan for you. A pathologist will study your tumor tissue and lymph nodes in order to accurately stage the cancer. The stage is based on the size and location of the main tumor, as well as how much it's spread to other parts of the body (such as nearby lymph nodes and other organs).
When breast cancer is caught early (stage I), the five-year survival rate is over 99 percent1. This reinforces the importance of regular self-exams and screenings.
Stages 0 through III are early-stage breast cancers
Stage IV is advanced-stage breast cancer
Breast Cancer Treatment Options
Breast cancer is often approached with a combination of treatments and therapies. Your personalized treatment plan will depend on a few factors:
- What stage of breast cancer you have
- What type of breast cancer you have
- Your personal and family health history
Meeting with your oncologist can be overwhelming and confusing. However, it's important to ask your provider questions and do your own research about treating breast cancer. Bring a friend or family member with you to your appointments who can help take notes.

Surgery - Lumpectomy or Mastectomy
The first step in treating breast cancer is often surgery. This includes a lumpectomy or mastectomy. Surgery is an effective way to remove cancerous tumors and breast tissue and can lower the risk of cancer coming back. Individuals who undergo surgery will face some recovery time and may need additional therapy or treatments depending on their type of cancer.
A lumpectomy is the removal of the cancerous tumor or tissue. It allows you to keep much of the breast as is. It's a less extensive surgery and individuals often go home the same day. With a lumpectomy, most women will also need to have radiation therapy for several weeks.
A mastectomy removes the entire breast. It's a major surgery but is very effective at treating breast cancer, especially in the early stages. It may or may not require radiation therapy afterwards. Women usually stay at least one night in the hospital after a mastectomy, and recovery can be more intensive.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is usually done in addition to surgery. It's delivered in a very precise way, aiming to kill only the cancer cells. Radiation is tailored to the type of tumor and surgery you had. It's also based on your breast and chest shape. During a planning session, the radiation oncologist will use a CT scan or MRI to plan and administer the radiation fields. They may put small marks on your skin to make sure the radiation is delivered in the correct position.
The length of your radiation treatment will depend on your breast cancer history. Most women receive radiation once a day, five days a week for 1 to 6 weeks.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be used to treat certain stages and types of breast cancer tumors. Chemotherapy drugs are very effective at killing or disabling cancerous cells.
Additional Therapies
Hormone Therapy
Targeted Therapy
Immunotherapy
Breast Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Each type of breast cancer treatment has possible side effects. Depending on the treatment, side effects may include:
- Pain
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Soreness
- Hormonal side effects (such as hot flashes)
- Hair loss
Remember that your provider has recommended your treatment because they felt the benefits outweighed the side effects. Let your doctor know if side effects don't feel manageable.
How can I manage breast cancer treatment side effects?
Side effect management may involve some trial and error, including:
- Anti-nausea medications
- Pain relief medicine (such as ibuprofen)
- Movement or exercise
- Rest
- A healthy diet
Keep track of any side effects you have and make sure your health care team is informed so they can help you manage side effects. They may be able to recommend medications that make you more comfortable, so you can continue on your treatment plan. (For example, not taking an anti-nausea medication can lead to vomiting and dehydration, which may interfere with your cancer treatment plan.)
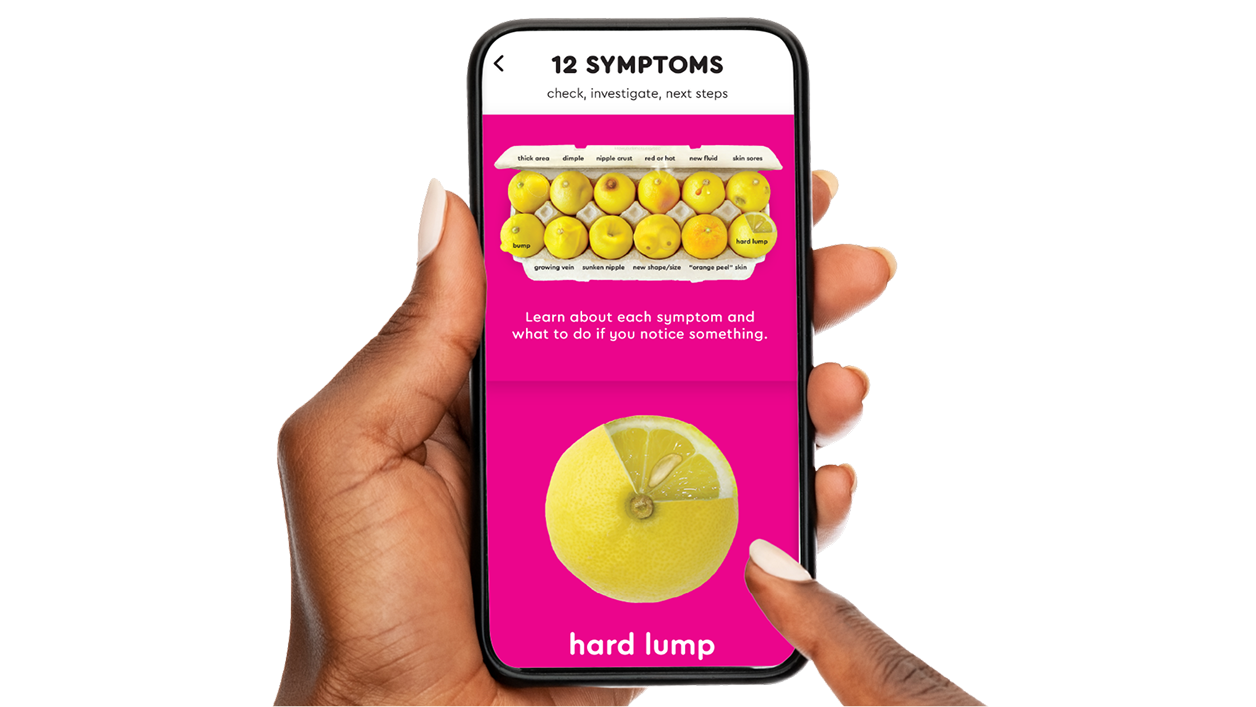
Better Early Breast Cancer Detection with the Know Your Lemons App
Are you confident about performing self-breast exams? The Know Your Lemons app can improve your chances of finding breast cancer early. Features include:
- Self-exam audio guide, video, and report
- Custom screening plan
- Period tracker
- Mammogram scheduler
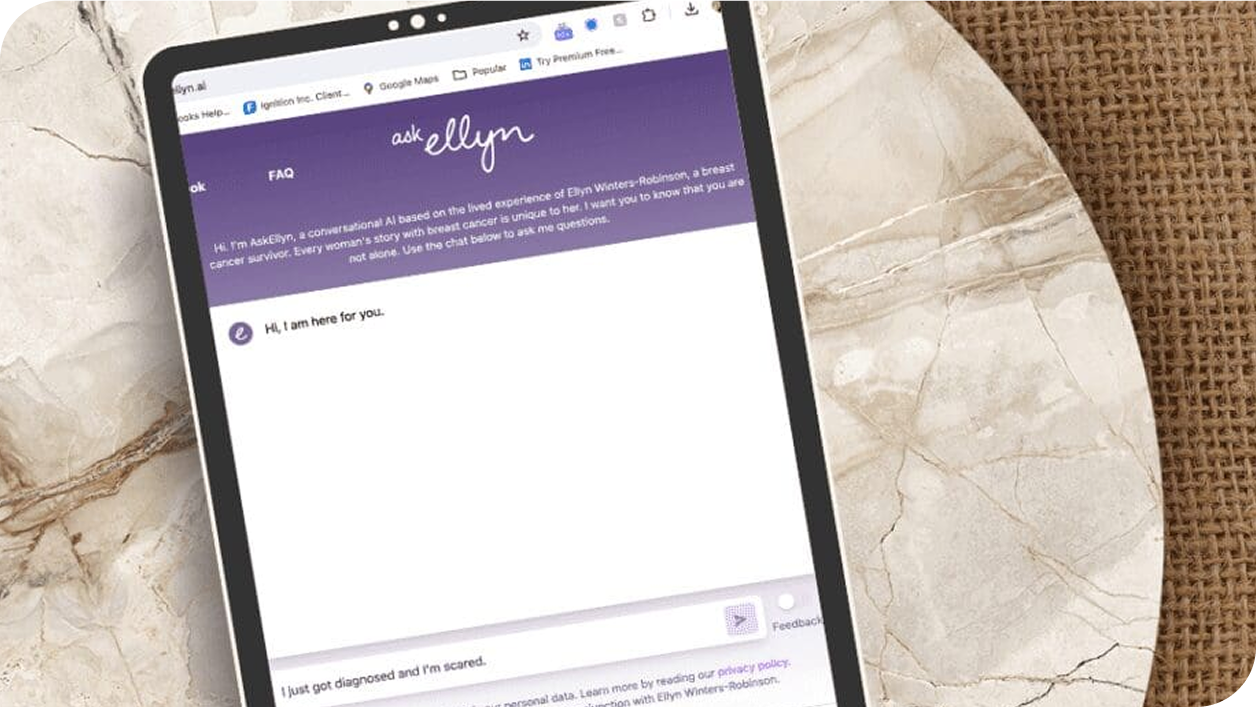
AskEllyn.ai: A Companion for Your Breast Cancer Journey
Whether you were just diagnosed, are going through treatment, or have a loved one with breast cancer, you deserve support. AskEllyn.ai is a free AI companion, available 24/7. Ask questions or simply receive comfort in this private and unique chat experience.
Are you a Cigna Healthcare member?
Access your benefits, discover mental and emotional support services, find in-network providers, manage your claims, and more.
Log in or activate your myCigna account to find your benefits
Discover more Cigna Healthcare member benefits
Not a Cigna Healthcare member? We're here to help.
Even if you're not a Cigna Healthcare member, there are many resources available to you to assist you on your breast cancer journey. Make sure to contact your insurance company to learn what cancer care benefits and services are available to you.
Tags
1 American Cancer Society, Survival Rates for Breast Cancer, https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/understanding-a-breast-cancer-diagnosis/breast-cancer-survival-rates.html, last revised January 16, 2025
All Cigna Healthcare® products and services are provided exclusively by or through operating subsidiaries of Cigna Healthcare, including Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company, or their affiliates. The Cigna Healthcare name, logo, and other Cigna Healthcare marks are owned by The Cigna Group® Intellectual Property, Inc.
The content provided on this web site is not medical advice and is not a substitute for medical care provided by a physician.
AskEllyn
I want to...
Audiences
Manage Your Account
Cigna Healthcare Information
The Cigna Group Information
Disclaimer
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Florida, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see a listing of the legal entities that insure or administer group HMO, dental HMO, and other products or services in your state). Accidental Injury, Critical Illness, and Hospital Care plans or insurance policies are distributed exclusively by or through operating subsidiaries of The Cigna Group, are administered by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company, and are insured by either (i) Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (Bloomfield, CT). The Cigna Healthcare name, logo, and other Cigna Healthcare marks are owned by The Cigna Group Intellectual Property, Inc.
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna Healthcare sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.
La aseguradora publica el formulario traducido para fines informativos y la versión en inglés prevalece para fines de solicitud e interpretación.
The insurer is issuing the translated form on an informational basis and the English version is controlling for the purposes of application and interpretation.